What is the difference between PX, EM, REM,%, VW and VH?
> Introduction to Elementor
- Basic structure of an HTML document
- Elementor units of measure
- Absolute units
- Relative units
- What is the difference between MS and REM?
- So what about %, VW and VH? What are they about?
- More about VW and VH
- When should I use one unit over another?
Basic structure of an HTML document
As Carl Sagan said, “If you want to make an apple pie from scratch, you have to invent the universe first.”And yes, in order to understand relative units of Elementor, what is a parent element or the root container, etc., we first need to know how a web page is basically structured in HTML language.
Here we see the minimal structure of an HTML (Hypertext Markup Language) document, the HTML language is composed of tags that are delimited by the lesser signs that are used in the HTML document. < and greater than >example <html>with exceptions such as the first label <!DOCTYPE html> which is absolute, all tags have opening and closing, e.g. <h1>Header</h1>, the closing is distinguished because the opening of the tag includes </ in addition to the “less than” slash also called slash /.

- The first line of the example is an absolute element (it has no closing tag); it is a document type declaration (also called DOCTYPE statement ) that identifies this document as an HTML5 document and lets modern browsers know that they must interpret the document as written in accordance with the HTML5 specification.
- The entire document is contained within an html document. The html is called root element because it contains all the elements of the document and cannot be included in any other element.
- Within html, the document is divided into a head and a body. The head contains descriptive information about the document itself, such as its title, the style sheets it uses, scripts and other types of “meta” information.
- The body is the body of the page, it is the element that contains everything we want to appear in the browser window.
- The meta elements within the head tag provide information about the document itself. A meta element can be used to provide all kinds of information, but in the case of this example it specifies the character encoding (the standardized collection of letters, numbers and symbols) used in the document.
- Inside the head there is also the mandatory title tag. According to the HTML specification, each document must contain a descriptive title. It is this title that is displayed in the browser tab and that Google will show in the search listing as the title of this page.
- Within the body block we can create as many sections as we want, the div tag, this tag allows us to group several block elements (paragraphs, headings, lists, etc). These sections are containers.
- It is another section like the previous one.
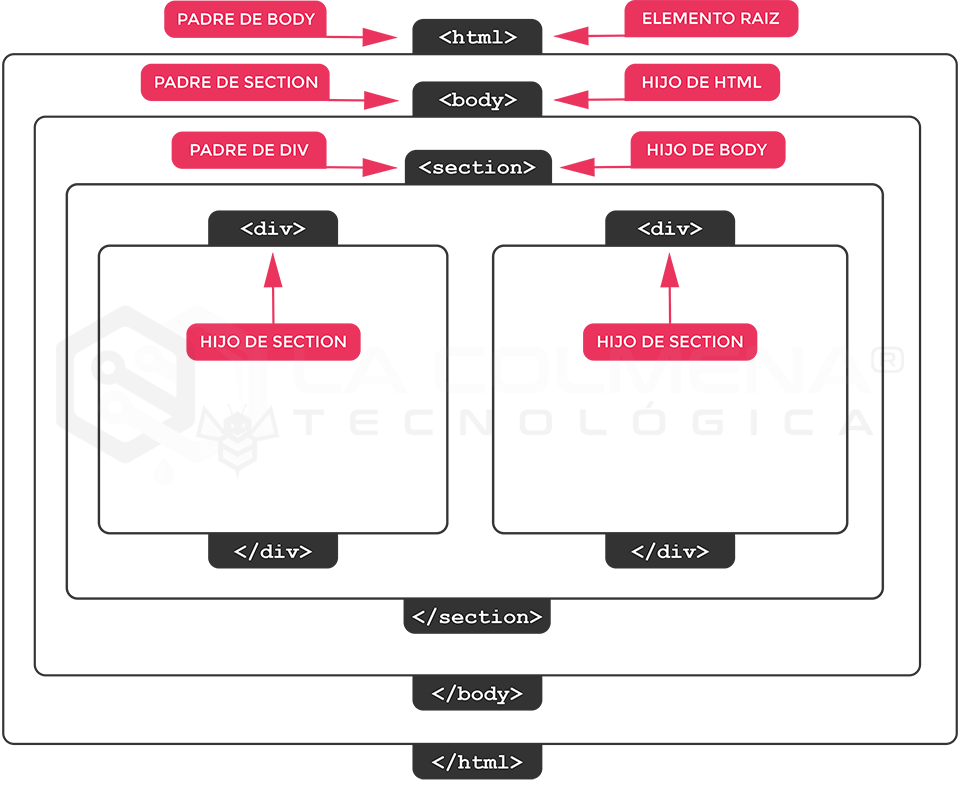
As you can see in the Figure, all these tags are like a kind of containers, the root or main tag is the html tag that contains all the others, inside html we have the body, and in turn inside the body we have other div. So we can say that the root element is html, body is a child of html and divs are children of body.
Elementor units of measure
When designing with Elementor, you can see that some elements have sizing options, allowing you to choose PX, EM, REM,%, VW or VH. But what do these units of measurement really mean and when should you use one or the other?
Let’s start with the basics, in CSS, you can specify sizes or lengths of elements using various units of measurement. The units of measurement you will find in some Elementor widget options include PX, EM, REM, %, VW and VH, although there are several more available in CSS. Not all Elementor elements will offer all of these units. Elementor only presents the options that make the most sense for the given element.
The most important aspect to learn about the different units is that some units, such as PX, are absolute units and others are relative units.
Absolute units
PX: pixels (px) are considered absolute units, although they are relative to the DPI and resolution of the display device. But in the device itself, the PX unit is fixed and does not change depending on any other element. The use of PX can be problematic for responsive websites, but they are useful for maintaining a consistent size for some elements. If you have elements that should not be resized, then using PX is a good option.
Relative units
- EM: relative to the parent element
- REM: relative to the root element (HTML tag and, failing that, the size configured by the browser).
- %: relative to the parent element
- VW: relative to the graphic window width
- VH: relative to the height of the graphics window
Unlike PX, relative units such as %, EM and REM are better suited to responsive design and also help to comply with accessibility standards. Relative units scale better on different devices because they can scale up and down according to the size of another element.
Let’s look at a simple example, in most browsers, the default font size is 16px. Relative units calculate the size from this base. If you change that base by setting a base size for the HTML tag through CSS, that becomes the basis for calculating the relative units on the rest of the page. Similarly, if a user adjusts their font size, that becomes the basis for calculating relative units.
So what do these units mean when it comes to the default value of 16px?
The number you specify will multiply that number by the default size.
1em = 16px (1 * 16)
2em = 32 px (2 * 16)
0.5em = 8px (.5 * 16)
1rem = 16 px
2rem = 32px
0.5rem = 8px
100% = 16 px
200% = 32 px
50% = 8 px
Okay, great, but what if the user changes the default size in their browser? Because these are relative units, the final size values will be based on the new base size. Although the browser default is usually 16px, if the user were to change it to 14px, the calculated sizes would end up being:
1em = 14px (1 * 14)
2em = 28px (2 * 14)
0.5em = 7px (.5 * 14)
1rem = 14px
2rem = 28px
0.5rem = 7px
100% = 14 px
200% = 28 px
50% = 7px
This gives the user the freedom to adjust the default font size of their browser, while maintaining the relative scale of each element they have specified.
What is the difference between MS and REM?
Looking at the graph above, it shows EM and REM looking exactly the same. So how do they differ?
In short, they differ according to heredity. As mentioned, REM is based on the root element (HTML) and in its default if it is not set to the user’s browser, which defaults to 16px. Each child element using REM will use the HTML root size as the calculation point, regardless of whether or not a parent element has different sizes specified.
EM, on the other hand, is based on the font size of the main element. If a main element has a different size than the root element, the EM calculation will be based on the main element and not on the root element. This means that nested elements that use EM for sizing can sometimes end up having a size that you did not anticipate. On the other hand, it gives you more detailed control if you need to specify the size of a particular area of a page.
So what about %, VW and VH? What are they about?
While PX, EM and REM are mainly used for font size, %, VW and VH are mainly used for margins, padding, spacing and widths/heights.
To reiterate, VH stands for “viewport height”, which is the height of the visible screen. 100VH would represent 100% of the viewport height or the full height of the screen. And, of course, VW stands for “viewport width”, which is the width of the visible screen. 100VW would represent 100% of the width of the graphic window or the full width of the screen. % reflects a percentage of the size of the main element, regardless of the size of the graphic window.
Let’s look at some examples of where Elementor offers %, VW and VH options.
- Column widths: if you edit the layout of an Elementor column, you will notice that there is only one width size unit available: %. Column widths only work well and responsively when percentages are used, so no other options are offered.
- Margins: the margins of a section can be specified in PX or %. Generally, it is preferable to use % to ensure that the margins are not larger than the content when scaling down for a mobile device, for example. By using a percentage of the device width, your margins will remain in relation to the size of the content, which is almost always preferable.
- Padding: the padding of a section can be specified in PX, EM or %. As with margins, it is often preferable to use EM or % so that padding remains relative as page size increases.
- Font size: if you edit the typography of an element, such as a header, you will see four options: PX, EM, REM and VH.
Have you ever created a large header and admired how great it looked on desktop, only to realize it was too big on mobile?
The key to solving this elegantly is to use EM, REM or VW instead of PX. What you choose depends on your particular situation. I usually choose EM because I want the size to be relative to the parent of the header. But if you prefer the size to be relative to the root size (HTML), choose REM instead. Or, you can set it to be relative to the width of the graphic window (VW) if that works better for your case.
Note that you can also set device-specific font size PX values by using the device icons to specify a size for desktop, tablet and mobile device. But that still imposes limits on responsiveness and accessibility, so keep that in mind if you choose PX.
More about VW and VH
The units of the graphic window represent a percentage of the current browser graphic window (current browser size). While similar to percentage units, there is a difference. The units of the graphic window are calculated as a percentage of the current size of the browser graphic window. Percentage units, on the other hand, are calculated as a percentage of the main element, which may be different from the size of the graphic window.
Let’s consider an example of a 480px x 800px moving screen display window.
1 VW = 1% of the width of the graphic window (or 4.8 px)
50 VW = 50% of the width of the graphic window (or 240 px)
1 VH = 1% of the height of the graphic window (or 8px)
50 VH = 50% of the height of the graphic window (or 400 px)
If the size of the graphic window changes, the size of the element changes respectively.
When should I use one unit over another?
Ultimately, there is no perfect answer to this question. In general, it is often better to choose one of the relative units rather than PX so that your website has the best chance of representing a responsive design. However, choose PX if you need to ensure that an element never changes size at any breakpoint and remains the same regardless of whether a user has chosen a different default size. PX units guarantee consistent results even if that is not ideal.
- EM is relative to the font size of the parent element, so if you want to scale the size of the element based on the size of its parent use EM.
- REM is relative to the font size of the root (HTML) and if this is not set, the one configured by the browser will be used, so if you want to scale the size of the element according to the size of the root, no matter what the main size is, use REM. If you have used EM and are encountering sizing problems due to many nested elements, REM is probably the best choice.
- VW is useful for creating full-width (100%) elements that fill the entire width of the graphic window. Of course, you can use any percentage of the width of the graphic window to achieve other objectives, such as 50% for half the width, etc.
- VH is useful for creating full-height (100%) elements that fill the entire height of the viewport. Of course, you can use any percentage of the height of the graphic window to achieve other goals, such as 50% for half the height, etc.
- % is similar to VW and VH, but is not a length relative to the width or height of the graphic window. Instead, it is a percentage of the width or height of the parent element. Percentage units are often useful for setting margin widths, for example.
- Elementor makes it easy to choose the option that best suits your design. Ultimately, it’s your choice.

Subscribe and receive notices of new content
Related topics
Header and Footer template in Elementor
true
13:21
0.0/5
Introduction to Elementor, Templates
Anchor in Elementor links to own page
true
41:00
0.0/5
Advanced tab, Introduction to Elementor
Elementor global widget template
true
07:00
0.0/5
Introduction to Elementor, Templates
Global Colors, Global Fonts and Theme Styles in Elementor
true
10:31
0.0/5
Introduction to Elementor, Site settings
{{ reviewsTotal }}{{ options.labels.singularReviewCountLabel }}
{{ reviewsTotal }}{{ options.labels.pluralReviewCountLabel }}
{{ options.labels.newReviewButton }}
{{ userData.canReview.message }}